Migration Options Tab¶
How to Access
Migration Options tab.
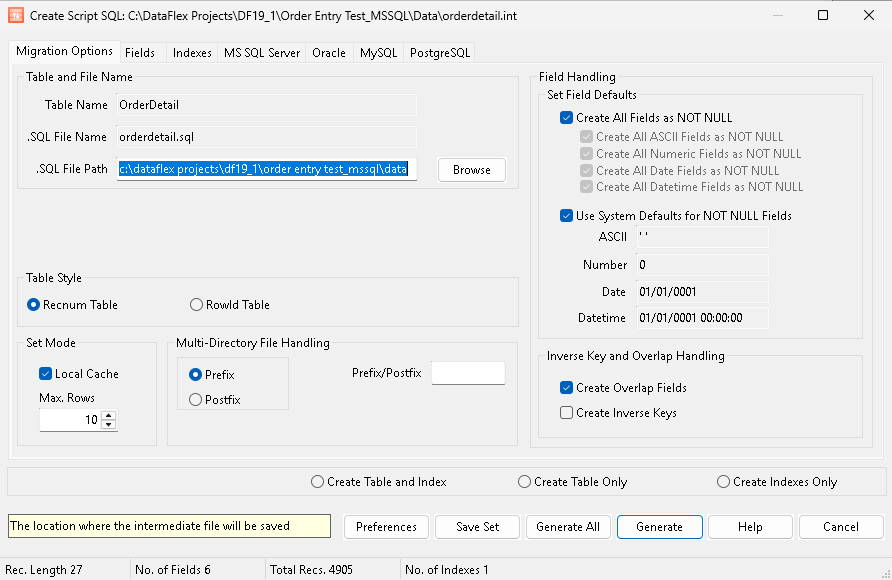
Table and File Name¶
Table Name: The name of the first selected table in the Filelist dialog with out any extension.
.SQL File Name: The name of the .int file that will be created (Table Name.sql).
.SQL File Path: The path to the file to the SQL script.
Table Style¶
Recnum Table: A RECNUM table emulates DataFlex record processing where a unique consecutive positive number (record number) is used to identify each record. The record number designates a record’s relative position in the table. This is useful for legacy applications.(DF_FILE_RECNUM_TABLE is true, the default)
RowId Table: A rowId table does not use RECNUM to uniquely identify a record, but instead relies on you specifying one or more fields that when combined create a unique record identity. Standard tables use the RowId concepts in Visual DataFlex instead of the older RECNUM concept. A RowId table can take advantage VDF RowId functions. (DF_FILE_RECNUM_TABLE is false)
See attribute DF_FILE_RECNUM_TABLE.
Set Mode¶
These setting are not used when creating a script. They are only used when creating an .INT file.
Multi-Directory File Handling¶
Used to handle creation of files with the same names in the current database.
It is common in the DataFlex and Pervasive environments to create files with the same name residing in different directories. For example each directory might be dedicated to a specific company, for example CompanyA/customer.dat and CompanyB/customer.dat. The DataFlex program knows based on the directory path, which file to access.
Mertech introduced the concept of “Table Suffix” or “Table Prefix” to support multi-company files. Each file name can now be assigned a custom prefix or postfix value to be prepended or appended to the file name. The table is created as “<prefix>RootName” or alternatively “RootName<postfix>” on the server. This approach allows different files to reside in the same database without conflict.
To specify a prefix, select the Prefix radio button and enter the prefix value. To specify a suffix, select the Suffix radio button and enter the suffix value.
File Handling¶
Set Field Defaults¶
NOT NULL fields
Create All Fields as NOT NULL: Checking this option automatically checks the Create all ASCII Fields as NOT NULL, the Create All Numeric Fields as NOT NULL, the Create all Date Fields as NOT NULL and Create all Datetime Fields as NOT NULL options. Unchecking it allows to to select which column type to set as NOT NULL.
Create All ASCII Fields as NOT NULL: If checked, all fields of type ASCII will be set to NOT NULL.
Create All Numeric Fields as NOT NULL: If checked, all fields of type numeric will be set to NOT NULL.
Create All Date Fields as NOT NULL: If checked, all fields of type Date will be set to NOT NULL.
Create All Datetime Fields as NOT NULL: If checked, all fields of type DateType will be set to NOT NULL.
Default values for NOT NULL fields When a field is created as NOT NULL, SQL databases expect a default value.
Use System Defaults for NOT NULL fields: If checked, the default value of the system will be used for all datatypes and the forms underneath will be disabled. Unchecked, the forms become enabled and you can change the default value to be used.
The System Defaults are as follows
ASCII: ASCII fields have default value of a single space.
Number: Numeric fields have a default value of 0.
Datetime: The default format for datetime fields depends on the configured date format (for example, military, US, or European) for the computer on which the application runs. The difference between these formats is the order of the fields. For example, yyyy-mm-dd vs. dd-mm-yyyy. The default datetime value, shown as (yyyy-mm-dd) is:
Driver Type |
Native Date Form |
Format/Value |
|---|---|---|
MySQL Windows v12.0 and above |
All |
0000-00-00 00:00:00 |
MySQL SCO v11.0 and above |
All |
0000-00-00 00:00:00 |
earlier versions of the MySQL |
All |
0001-01-01 00:00:00 |
PostgreSQL |
All |
0001-01-01 00:00:00 |
Oracle |
All |
0001-01-01 00:00:00 |
MS SQL |
DATETIME |
1753/01/01 00:00:00 |
MS SQL |
SMALLDATETIME |
1900/01/01 00:00:00 |
MS SQL |
All other formats |
0001/01/01 00:00:00 |
If Use System Defaults for NOT NULL fields is unchecked, the user can enter custom values:
ASCII: Enter the default value for all NOT NULL ASCII fields. Disabled if Use System Defaults for NOT NULL fields is checked.
Number: Enter the default value for all NOT NULL number fields. Disabled if Use System Defaults for NOT NULL fields is checked.
Date: Enter the default value for all NOT NULL date fields. Disabled if Use System Defaults for NOT NULL fields is checked.
DateTime: Enter the default value for all NOT NULL Datetime fields. Disabled if Use System Defaults for NOT NULL fields is checked.
This cooresponds to the Classic Attribute DF_FIELD_DEFAULT_VALUE.
Inverse Key and Overlap Handling¶
Create Overlap Fields: When checked, this option creates another column with information for the index when there is a partial overlap. This option improves performance.
Create Inverse Keys: When checked, Mertech’s driver creates additional columns called inverse key columns that handle case sensitive indexes and descending index segments. Selecting this option creates the inverse key columns. This option is turned on by default.
Bottom Controls¶
The controls at the bottom of the dialog remain the same regardless of the tab selected.
